It’s that time of year again! Temperatures are colder, leaves have fallen and pumpkins are carved. Things are a bit spookier, but it’s a good time to remind ourselves that SEO isn’t all that scary. Just because Google has several updates throughout the year and is a bit unpredictable at times does not mean you need to be afraid of organic search and growing your SEO.
However, with that said, we do see some spooky things happening in the SEO space on a relatively frequent basis that you should be aware of.
Below are 8 of the most frightening on-page and off-page things to be aware of in SEO. Read on if you dare…
QUICK LINKS
- 1. Disturbing Duplicate Content
- 2. Creepy Canonical Tags
- 3. Treacherous Title Tags
- 4. Ghastly GTMetrix Scores
- 5. Heinous Header Tags
- 6. Hellacious Hierarchies & Unruly URL Structures
- 7. Repulsive Robots.txt Files
- 8. Sinister Link Spam
Scary Things to Avoid in SEO
1. Disturbing Duplicate Content
Duplicate content is an SEO’s favorite nightmare to work with. It’s very common for a website owner to take inspiration from other websites to fill in their own content and we come across this all of the time. Unfortunately, Google frowns upon this practice and upon plagiarism as a whole.
No matter the type of site you operate, it’s critical to create unique content for every page and to avoid lifting content from any other website. Even if you have explicit permission to use content from another website, just know that Google will consider it plagiarism and can limit your ranking potential because of it.
We commonly see this practice happen on e-commerce websites that use a manufacturer’s description for products. Because the description has already been published online (by the manufacturer and other retail websites), it’s considered duplicate content to Google. Additionally, we run into websites with internal duplicate content where certain page sections or an entire page’s content is found on multiple URLs of a site. When this exists, Google doesn’t know which content to rank in search results and it has an effect on organic traffic.
Steer clear of duplicate content to stay on Google’s good side. You can take ideas from other websites, but make sure they are rewritten and published in a unique way.
2. Creepy Canonicals
What’s a good solution to internal duplicate content on a site? Use canonical tags.
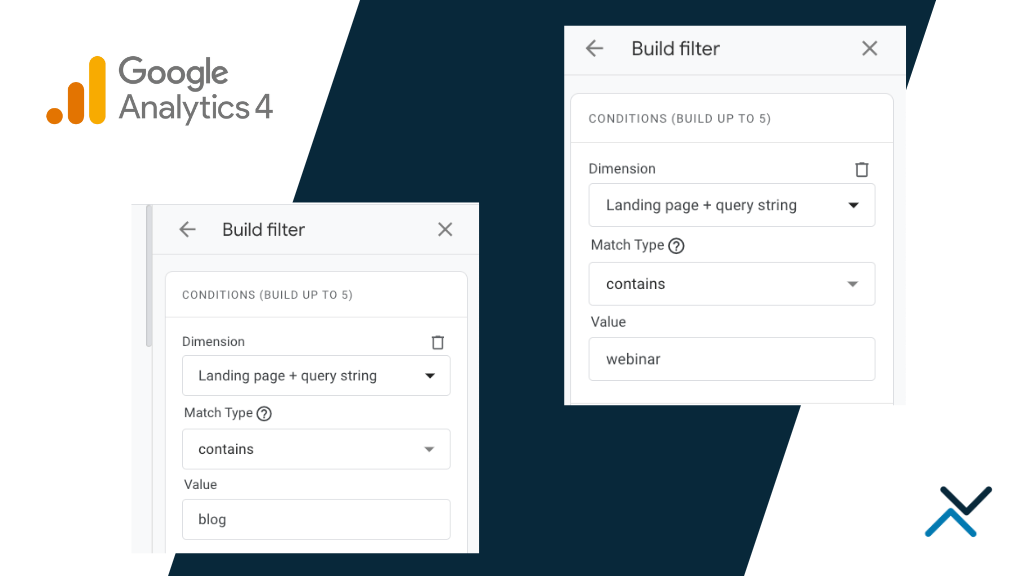
Canonical tags are used anytime a website has multiple versions of the same content, but we want Google to index and rank only one version of the content. This happens often in e-commerce SEO where content can be accessed through a number of different URLs used to sort and filter product results.
Be Cautious with Faceted Navigation
For instance, a user will see the same content by accessing example.com/shirts/?size=large&color=blue and example.com/shirts/?size=large&color=blue&sort=by_price – the visual content may change slightly with the additional sorting parameter in the second URL, but the overall content of the page does not change.
Additionally, in most e-commerce websites, key on-page elements like heading tags, title tags and page copy won’t change just because a parameter is added. For this reason, we leverage canonical tags to point up to the parent directory; in this case above, it would be example.com/shirts/. This informs Google that it should index and rank the parent category and not all the variations the user can find. This type of faceted navigation is often helpful to the shopper but can create issues for search engines where they can sometimes get trapped.
Canonical tags are a technical SEO element and need to be implemented in the right spot of the page. Of course, the creepiest issue we see with canonical tags is incorrect placement in the source. As advised by Google, a rel=”canonical” tag should be placed above the closing </head> tag. If you place this tag within the <body> tag, Google will miss the signal completely. It’s also important to remember that a canonical tag is only a suggestion to search engines and they are not always followed. If you operate an e-commerce website with opportunities for duplicate content to exist, you may want to use rel=”nofollow” on certain facets and sorting rules too to limit Google from crawling too many URLs.
Be careful with your canonicals and don’t let a search engine get stuck!
3. Treacherous Title Tags
A title tag is what shows as the headline in search results. This tag is important for Google and other search engines to understand what the page is about. You need a title tag to accurately describe the page and it can help users click through from the SERP. What you don’t need to do is spam the title tag with every keyword you’re trying to optimize for. While keywords are important in the title tag, just know that spamming the title with keywords and going over the recommended character count (~70 characters) will not help your SEO.
A good title tag should include the most important topic of the page (which is usually similar to the H1 tag on the page) and the site’s name / brand name. You should avoid stuffing too many keywords in the title or Google could see it as spammy and not rank the page. Additionally, the character length shouldn’t exceed 70 characters or Google could choose to truncate it.
In the example above, this local plumber’s website is using too many keywords in the title, doesn’t reference the brand name and it clearly looks spammy. As such, it ranks on the 6th page of search results for its target keyword and is seemingly ignored by Google. Try to craft title tags that meet SEO requirements and will entice a user to click through to your content. As with any content you create, write first for human readers and second for robots.
4. Ghastly GTMetrix Scores
Google introduced its Core Web Vitals algorithm update in June of 2021 with an emphasis on website speed and user experience. The speed of a website is a vital factor to the user’s experience and should always be optimized to be as fast as possible. When a website is too slow by Google’s standards, it’s too slow for users and will not be a good site to show in search results. A site can become slow because of large media files, images that have not been compressed properly for a web browser, CSS, Javascript and HTML files filled with excessive white space or certain snippets of code that cause a delay in the page loading.
As a result of a slow site, tools like GTMetrix will give it a low grade that corresponds to how Google views the site. We often see sites with low scores rank lower than sites with a faster experience.
In the example below, we see a website with a low performance score and cumulative layout shift. These two components are essential to Core Web Vitals and should be optimized to improve the user’s experience on the site.
If you have a ghastly website score from GTMetrix in the range of D, E or F, you need to consider speed improvements for your website. Not only do you benefit from a faster site from an SEO perspective and comply with Google’s Core Web Vitals, you’ll also give your users a faster experience they will appreciate.
5. Heinous Header Tags
As another key on-page element, it’s important to have well-structured heading tags on your pages. Heading tags refer to content wrapped in <H1>, <H2> and <H3> and should follow a logical structure. For example, your page’s content should begin with the primary topic of the page followed by subtopics in a way that makes sense to readers. The primary topic of the page is perhaps the most important and therefore should appear at the beginning of the page to the user and within the source code, appropriately wrapped in an H1 tag. Not only does this tell visitors what the main topic of the page is, but it also gives search engines a better idea of what your content is about.
When structuring the content of your page, avoid placing secondary heading tags above the H1 tag of the page. This can create confusion as to the primary topic of the page for both users and search engine crawlers. Additionally, it’s best practice to use one H1 tag to highly the primary topic of the page. While Google’s John Mueller has claimed, “our systems don’t have a problem when it comes to multiple H1 headings on a page,” we recommend trying to stick to one main header per page followed by secondary headers for subtopics.
One of the most heinous things we run into with header tags is when they are completely non-existent on a website. Several web developers will style <p>, <div> and <span> tags to look like headings on a page without the content actually being wrapped in a heading tag. While it may look great to users, it will not appear as a heading to search engines and may be treated as another paragraph of text. Break up your content with appropriate heading tags and make it easy for search engines to understand your content.
6. Hellacious Hierarchies & Unruly URL Structures
A hierarchy refers to how content is organized within a site and how it relates to other areas of the site. Whether it is an e-commerce website or a strictly informational website, it’s important to house your content within a logical taxonomy that makes sense for users and for search engines. The site’s hierarchy will also correlate to things like URL structure (folder paths that appear in the URL) and breadcrumbs shown in search results.
As an example, if you operate a medical website with different service categories for the types of care you provide for patients, you will want to organize your content under a “services” hierarchy.
Here you would have URLs like example.com/services/service-a/, example.com/services/service-b/, example.com/services/services-c/, etc. Likewise, for e-commerce websites with a variety of different product categories, try to organize your subcategories in an easy-to-understand manner. As an example, if your website sells office furniture, you will want to organize product hierarchies like example.com/office-furniture/chairs/ and example.com/office-furniture/desks/. This structure makes it easy for users to know where they are going and offers a clean structure for Google.
In the example below, you can see that the Water Soluble CBD product is associated to a larger category of Products, and it appears in Google’s search results as a breadcrumb. This makes it easy for the search engine to know where the page lives and how it fits in with the rest of the site’s content. We also make the URL easy to understand as https://www.laurelcrest.com/products/water-soluble/, where both Google and the user know exactly what the content is and how it fits into the site.
The most hellacious issues we see when it comes to website hierarchies are pages with no hierarchy whatsoever or pages with the complete wrong hierarchy. When this happens, pages can easily become orphaned and will have little relevance to Google. Organize your pages in a way that makes sense for your users, doesn’t allow for orphaned content and is easy to access for search engines. Remember, if a site’s hierarchy can be confusing to a user, it will be confusing to a search engine.
7. Repulsive Robots.txt Directives
A robots.txt file is essentially the key to allowing Google and other search engines to crawl your site. While a web crawler can find a website in a number of ways, a properly implemented robots.txt file gives permission for a bot to crawl the website. Because this file is a relatively technical SEO implementation, it can also cause several issues when it is not properly implemented.
One of the most repulsive things we run into with robots.txt files is when the file blocks all access to a website through a disallow directive. A simple disallow directive that is usually put in place to block search engines from certain pages (i.e., customer account pages, reset password pages, cart pages, etc.) has the ability to block all bots entirely. This unintentionally tells search engine crawlers to go away and not crawl or index the content of the page. And if a web crawler can’t successfully read the content of a page, good luck getting it indexed and ranking in Google.
Be sure to check your robots.txt file to ensure Google is not repulsed by your directives. And make access to your pages even easier for Google by linking directly to your XML sitemap from your robots.txt file.
8. Sinister Link Spam
Stepping away from common on-page SEO mishaps, we often find ourselves reviewing link spam and its impact on a site’s rankings.
Most SEO strategies focus on the on-page improvements first, followed by content enhancements and finally, a link development campaign. Building links to a website is by far the most time-consuming part of an SEO’s job and should never be addressed with low-effort, ineffective or spammy link tactics.
At a high level, it’s important to remember that if a link is easy to acquire for anyone with little effort, how valuable can it really be? A lot of links we come across are from spammed websites where value is not truly being passed, the link belongs to a private blog network or the link has no relevance to the client’s site. This is often the result of cheap SEO that doesn’t have lasting results and can land a site in the penalty box with Google. These tactics might work initially, but they have the potential to bury a website.
While Google does a good job at negating spammy links for websites and it is known that Google Penguin is now part of its core algorithm, it is still important to keep a watchful eye on your link profile.
Most SEO tools provide a spam score (pictured above from Moz) and will show you links that could have a negative impact on your rankings. If you notice sinister-looking links pointing to your website that drive a high spam score, be sure to address them as soon as possible to avoid losing organic traffic. Likewise, avoid acquiring links from any suspicious websites, private blog networks or any sites that have little relevance to yours.
Let’s Get to Trick Or Treating
These 8 areas of SEO only scratch the surface of what can go wrong.
It’s important to implement the right technical SEO optimizations, enhance your content without being spammy and acquire links that are relevant to your website. Also, remember these different SEO elements don’t happen in silos but instead work in conjunction with each other to achieve organic search success. Google changes things all of the time for us, but it’s nothing to be afraid of. Work with Google’s updates and find a strategy that works best for your site and budget.
Be careful and Happy Halloween from Octiv Digital!